Tropomyosin is a long, thin protein that helps regulate the interaction between actin and myosin filaments. It lies along the actin filaments and blocks the binding sites for myosin. When a nerve impulse triggers a muscle contraction, a molecule called calcium ions is released into the muscle cell. This causes troponin to bind to actin and move.. Once the calcium ions concentration falls below a certain level, no more contraction cycles can occur. The myosin-binding sites are hidden, and the skeletal muscle relaxes. Energy Sources. The contraction of skeletal muscle requires energy in the form of ATP. This ATP is used by muscle for three major purposes;

A2 5.5.9.2 Muscle contraction Diagram Quizlet

Cardiac muscle cell contraction (general) Physiology, Exercise physiology, Medical knowledge

thefatstudent “932pm// Sliding Filament Theory of muscle contraction poster to go on my
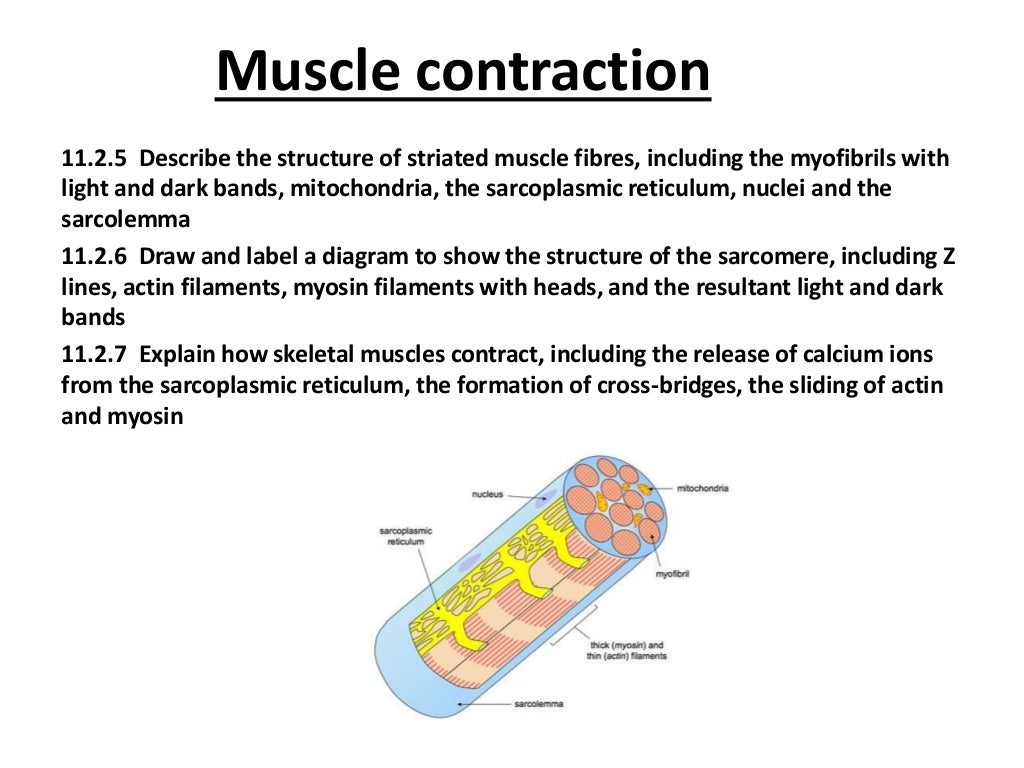
Muscle contraction Higher Level Biology IB
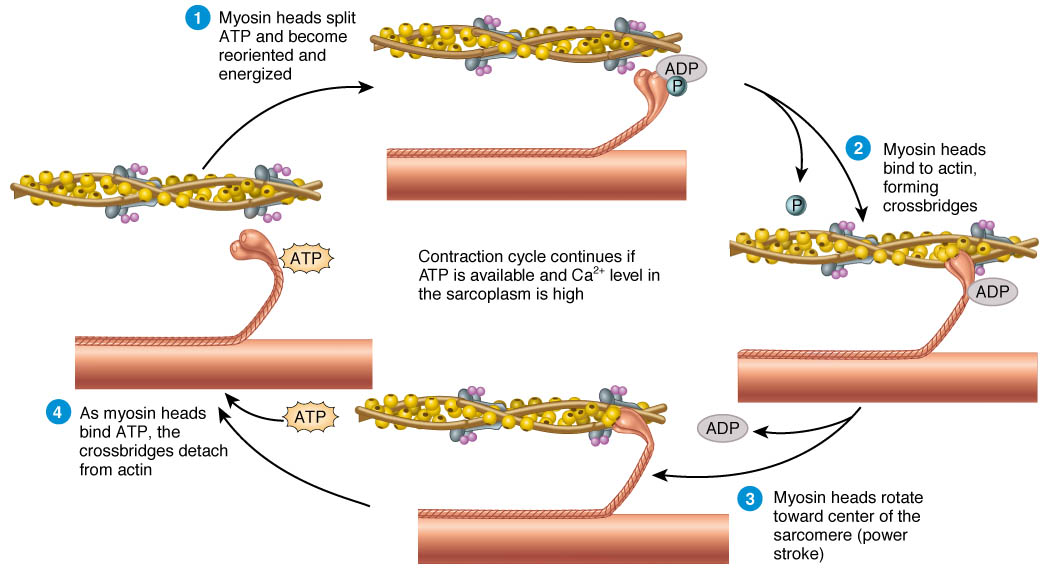
A Basic Look At How A Muscle Contracts
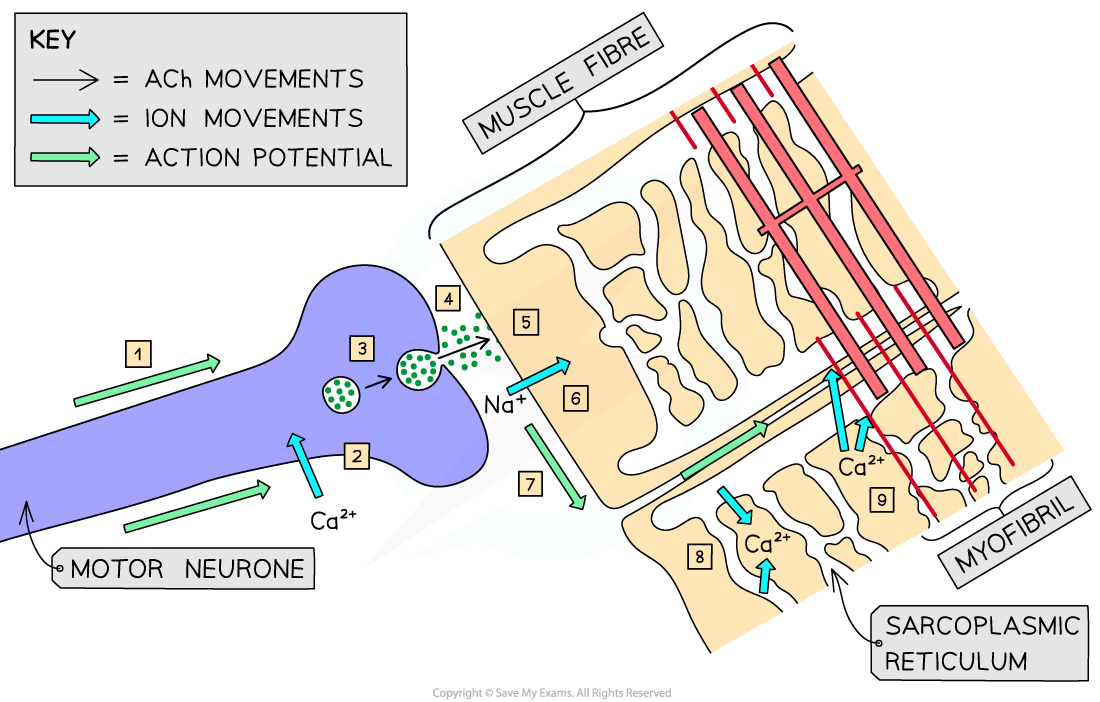
CIE A Level Biology复习笔记15.1.10 Stimulating Contraction in Striated Muscle翰林国际教育

muscle contraction Biology Notes, Science Notes, Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, Science

Explain the mechanism of muscle contraction with a diagram.

Musclular System Labeled Back Human Muscle System Functions Diagram Facts Britannica xaqukao7

12183.jpg

Neural Stimulation of Muscle Contraction Biology for Majors II

Muscle contraction Higher Level Biology IB

Muscle contraction Physiology, Study guide, Study biology

Image result for muscle cell Exercise Physiology, Anatomy And Physiology, Muscular System
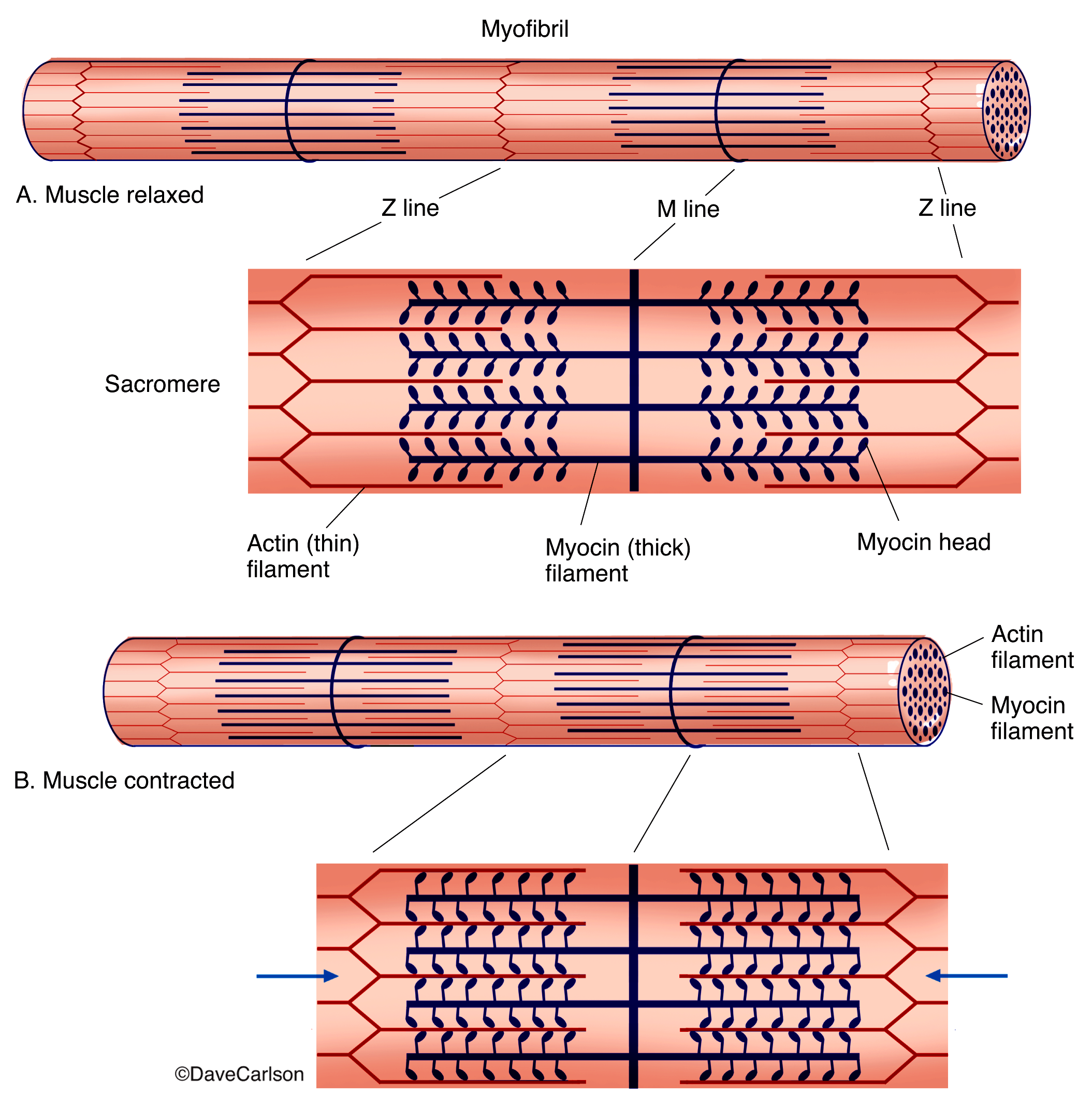
UDL Core Foundation Level 2 Learning Designed

A2 Biology Muscle Contraction Teaching Resources Biology worksheet, Flashcards revision, Biology
![Muscle Contraction Process Molecular Mechanism [3D Animation] (+playlist) Teaching biology Muscle Contraction Process Molecular Mechanism [3D Animation] (+playlist) Teaching biology](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/b7/fa/cb/b7facb0d9cf9cc968d8e339e95d477c6.jpg)
Muscle Contraction Process Molecular Mechanism [3D Animation] (+playlist) Teaching biology

FREE GCSE A Level Biology Muscle Contraction Practice Exam Question Teaching Resources

38.17 Muscle Contraction and ATP and Muscle Contraction Biology LibreTexts

Full Science Lessons by Theresa Teaching Resources TES
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 9, s6-s7 (2008) doi:10.1038/nrm2581. Goody, R. S. The missing link in the muscle cross-bridge cycle. Nature Structural Molecular Biology 10, 773-775 (2003.. This is known as the sliding filament model of muscle contraction and occurs via the following process: An action potential arrives at the neuromuscular junction. Calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Calcium ions bind to troponin molecules, stimulating them to change shape. This causes troponin and tropomyosin proteins.